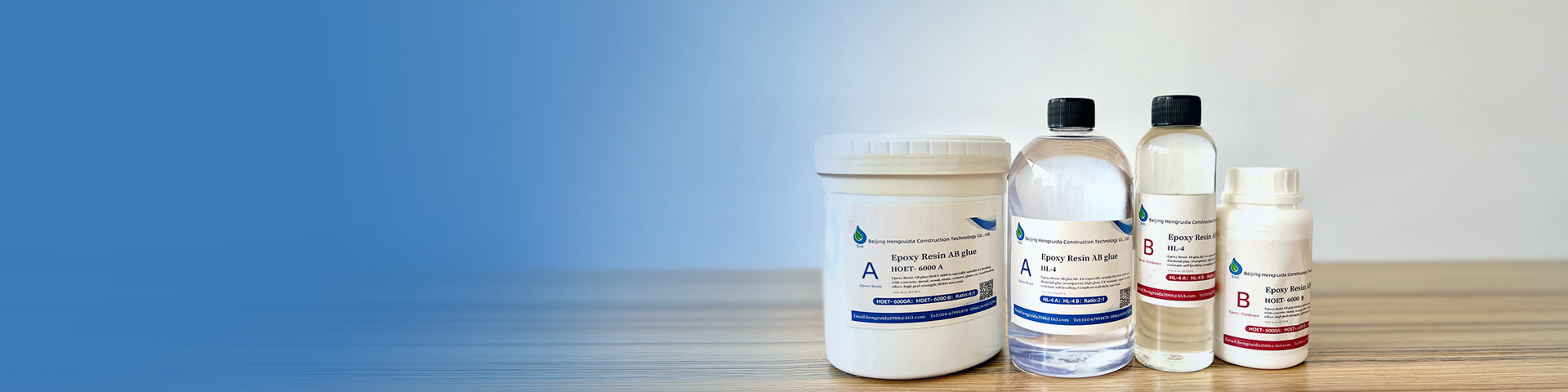
The key role and technological breakthrough of medical needle glue
In medical devices such as disposable syringes and indwelling needles, the bonding quality between the needle and the needle tube directly affects clinical safety. Traditional UV glue is limited by the requirement of transparent curing, while epoxy resin has gradually become the preferred material for bonding high-end medical needles due to its high strength, sterilization resistance, and biocompatibility. However, its modification needs to meet the strict standards in the field of medical devices.
Special requirements for medical scenarios
● Mandatory biocompatibility certification: requires passing ISO 10993-5 cytotoxicity, ISO 10993-10 irritation and sensitization tests, with a residual free bisphenol A content of less than 0.1ppm (according to USP Class VI standards).
● Resistant to extreme disinfection conditions: withstand high-pressure steam sterilization at 121 ℃ for 30 minutes, ethylene oxide (EO) fumigation, and repeated wiping with 75% alcohol. The adhesive strength attenuation rate should be less than 10%.
● Micro scale precision bonding: The inner diameter of the needle tube is usually ≤ 0.3mm, and the adhesive needs to achieve a uniform coating of 5-10 μ m thin layer. After curing, the volume shrinkage rate should be less than 0.5% to prevent microcracks.
Modification strategy of epoxy resin system
To meet medical compliance, targeted optimization needs to be carried out at the molecular design level:
● Biosafety improvement: Hydrogenated bisphenol A-type epoxy resin is used instead of traditional bisphenol A-type, combined with non migratory curing agents (such as modified cyclic amines), to increase the cytotoxicity rating from level III to level I (MTT assay shows cell survival rate>95%).
● High temperature water vapor synergistic modification: Introducing a hybrid structure of organic silicon and epoxy, forming a hydrophobic barrier in the cross-linked network, and increasing the shear strength retention rate from 62% to 89% after 1000 hours of wet heat aging (85 ℃/85% RH).
Nano level rheological control: Add 5% nano silica thixotropic agent to reduce the viscosity of the colloid to 50 mPa · s at a high shear rate of 10 ^ 4 s ⁻¹ (for easy needle infusion), with a static thixotropic index greater than 6.0 (to prevent overflow).
Adhesive of insulin injection pen needle
● The 31G ultra thin wall needle (wall thickness 0.1mm) using modified epoxy adhesive passed the 200N axial tensile test (YY/T 0806 standard),
● After being wiped with alcohol for more than 50 times, there is no debonding, which is better than the 30 time limit of traditional cyanoacrylate adhesive.
Fixation of indwelling needle and catheter
● Realize adhesive strength>15MPa at the needle hub catheter interface
● After 60 cycles of high-pressure sterilization, the microbial barrier integrity qualification rate was 100% (ASTM F2638 test).
Industry Development Trends
With the popularity of pre filled syringes (PFS), the new generation of epoxy medical adhesives is developing towards the direction of "zero curing stress". By using cationic ring opening polymerization technology (such as triarylthionium salt initiation system), a shrinkage rate of less than 0.1% can be achieved at a low temperature of 60 ℃, while meeting the requirement of rapid curing in 5 minutes, providing a more stable packaging solution for biological agent filling.







